
DSS awarded contract by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory to provide ROSA solar arrays for NASA’s DART Mission.
Santa Barbara, California, April 20, 2018 – Deployable Space Systems, Inc. (DSS), a leading supplier of innovative flexible blanket and rigid panel solar array systems, announced today that that it has been awarded a contract by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory for the design, analysis, manufacturing, testing, and delivery of Roll-Out Solar Arrays (ROSA) for NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) Mission.
 Artistic rendering of the DART spacecraft with ROSA solar arrays
Artistic rendering of the DART spacecraft with ROSA solar arrays
NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) mission will be the first-ever spacecraft to demonstrate asteroid deflection by kinetic impactor on an asteroid target. DART is planned to intercept the secondary member-or “moonlet”-of the Near-Earth Asteroid Didymos binary system in October 2022, changing the orbit of the moonlet around the primary asteroid while not altering the overall path of the pair around the Sun. Observations of the results of this impact by ground-based observatories (and possibly other spacecraft) will provide data on how effective this technique is. The DART mission is a critical step in understanding and demonstrating one of the approaches that could be used to protect Earth by changing the speed of a hazardous incoming asteroid, putting it into a different orbital flight path that would not threaten the planet.
DART is directed by NASA and led by a team at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory with support from NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, NASA Johnson Space Center, and the Jet Propulsion Laboratory. The project is overseen by the Planetary Missions Program Office at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The Planetary Defense Coordination Office within NASA’s Science Mission Directorate is the lead for planetary defense activities and is sponsoring the DART mission.
The ROSA solar array for the DART mission will provide more than 6.6 kilowatts of power at beginning-of-life, and is based on the ROSA solar array technology recently demonstrated on NASA’s International Space Station (ISS) in June 2017. The ROSA solar arrays will provide reliable and continuous power for NASA’s Evolutionary Xenon Thruster-Commercial (NEXT-C) ion drive system. ROSA’s power output coupled with NASA’s NEXT-C drive system will have, over significant time and interplanetary distances, the capability of reaching up to 324,000 kilometers per hour, more than five times faster than the speedy Voyager 1 probe.
The ROSA solar array technology was successfully flown on the ISS flight demonstration mission during June 2017. A photograph of the ROSA solar array deployed on ISS is shown below. A video compilation of the ROSA spaceflight demonstration mission is provided at the following link: https://vimeo.com/226383484
 ROSA Solar Array Demonstrated on ISS in June 2017
ROSA Solar Array Demonstrated on ISS in June 2017
The ROSA technology is currently being qualified by SSL, a Maxar Technologies company, for high power geostationary earth orbit (GEO) missions and space exploration missions. A photograph of the SSL GEO ROSA solar array qualification wing is shown below. “The ROSA technology is a key element in SSL’s future product roadmap and the company expects that it will be valuable in the increasingly competitive spacecraft marketplace both for commercial and U.S. government missions,” said Dr. Matteo Genna, Chief Technology Officer and Vice President, Product Strategy and Development at SSL.
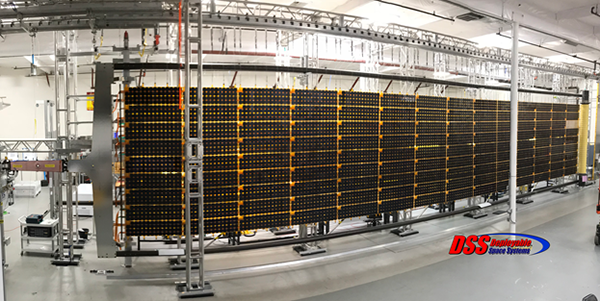 ROSA Solar Array Qualification Wing for SSL, a Maxar Technologies company, for High Power GEO Satellite and Space Exploration Missions
ROSA Solar Array Qualification Wing for SSL, a Maxar Technologies company, for High Power GEO Satellite and Space Exploration Missions
“DSS is proud to support NASA and The Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory with the innovative ROSA solar array system for this extraordinary DART mission, which will demonstrate and enable planetary protection for our precious Earth,” said Brian Spence, President of DSS. “For nearly a decade, DSS has been at the forefront of advanced solar array system technology development, manufacture and validation for the most demanding mission applications, including solar array systems for solar electric propulsion (SEP) missions such as DART. ROSA is the highly successful offspring of DSS’s significant technology development and commercial infusion initiatives. For this important DART program, and our NASA and Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory customers, DSS is further committed to maintaining ROSA as the highest quality, most affordable, and highest performance solar array system solution available.”
More information about NASA’s DART program:
The following animation shows how NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) mission would target and strike an asteroid, demonstrating how a kinetic impact could potentially redirect an asteroid as part of NASA’s planetary defense program.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8zooPRmgUPI
Additional information on the DART program can be found at the following websites:
http://dart.jhuapl.edu/
https://www.nasa.gov/planetarydefense/dart
About Deployable Space Systems, Inc. (DSS).
Deployable Space Systems, Inc. (DSS) is a leading provider of satellite deployable structure and solar array power solutions to the global space markets, encompassing a wide array of applications including civil space exploration, science and earth observation, defense intelligence and communication, and commercial telecommunications industries. The business was founded in 2008, is solely owned and operated, and is headquartered in Santa Barbara, California, USA. For more information about DSS, visit http://www.dss-space.com/
About the ROSA Solar Array
The multiple patented and award winning (2016 R&D-100 Award for Most Market Disruptive Technology) ROSA solar array technology is a new and innovative mission-enabling rolled flexible blanket solar array system that offers greatly improved performance over conventional rigid panel solar arrays and other state-of-the-art solar arrays, as well as greater affordability for use on future NASA, Air Force, and commercial space missions. The DSS ROSA solar array features an innovative “roll out” design which uses composite booms to serve as both the primary structural elements and the deployment actuator, and a modular photovoltaic blanket assembly that can be configured into a multitude of solar array architectures. The stored strain energy of the booms enforces the unrolling deployment actuation, and when fully deployed the rigid booms provide the solar arrays’ structural stiffness and strength. The ROSA technology achieves this simplicity without the use of complex mechanisms, intricate hinges or expensive motors/controllers typically associated with other competing solar array technologies. The ROSA solar array, when configured for launch, stows into a compact cylindrical volume yielding efficient space utilization. The unique ROSA stowed configuration is able to allow extremely large solar array deployed areas to be stowed very compactly for packaging within launch vehicles because its solar cells are mounted on an innovative rollable modular flexible blanket which is much thinner than traditional rigid panel solar arrays currently in use. SSL, a Maxar Technologies company, of Palo Alto, California is currently flight-qualifying and implementing DSS’s ROSA technology onto SSL’s heritage commercial satellite platform, enabling higher spacecraft power, enhanced payload capability, and improved solar array performance and affordability. ROSA is also currently being implemented on other proprietary flight programs with other customers, and is baseline on numerous proposed missions.




